Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women worldwide, with over 2 million new cases diagnosed each year. It is also the second leading cause of cancer death among women, after lung cancer. However, early detection and treatment can lead to very good outcomes for most women with breast cancer.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS): This is a non-invasive type of breast cancer that starts in the milk ducts but has not spread to the surrounding breast tissue. DCIS is often considered to be a pre-cancer, and it is usually treated with surgery or radiation therapy.
- Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC): This is the most common type of invasive breast cancer. It starts in the milk ducts and spreads to the surrounding breast tissue. IDC can be treated with surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy.
- Invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC): This is the second most common type of invasive breast cancer. It starts in the milk-producing glands (lobules) of the breast and spreads to the surrounding breast tissue. ILC is often treated in the same way as IDC.
Other types of breast cancer include:
- Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC): This is a rare but aggressive type of breast cancer that does not have estrogen receptors, progesterone receptors, or HER2 receptors. TNBC is often treated with chemotherapy and surgery.
- Inflammatory breast cancer (IBC): This is a rare type of breast cancer that causes the breast to become red, swollen, and warm. IBC is often treated with chemotherapy and surgery.
- Paget’s disease of the breast: This is a rare type of breast cancer that affects the skin of the nipple and areola. Paget’s disease is often treated with surgery and radiation therapy.
It is important to note that breast cancer can occur in men as well as women, but it is much less common in men.
What are the symptoms of breast cancer?
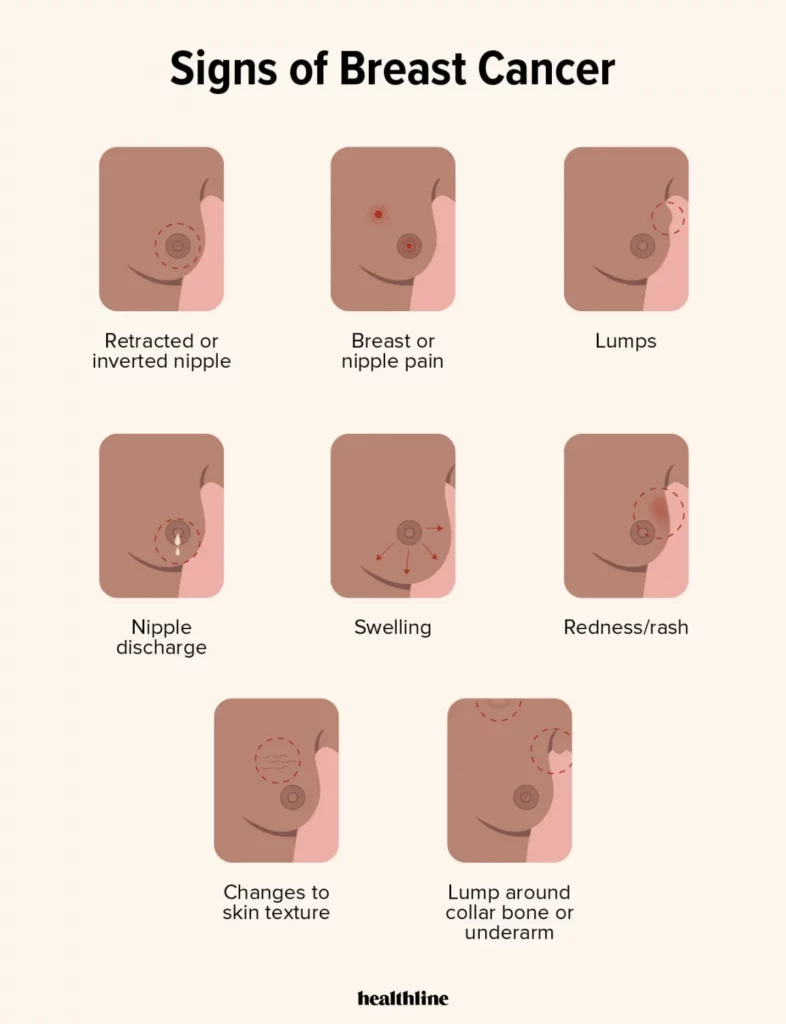
The most common symptom of breast cancer is a lump in the breast or underarm. Other symptoms may include:
- Changes in the size, shape, or texture of the breast
- Nipple discharge (other than breast milk)
- Nipple retraction (turning inward)
- Redness, dimpling, or puckering of the breast skin
- Pain in the breast or underarm
What causes breast cancer?
The exact cause of breast cancer is not known, but there are a number of risk factors that can increase your chances of developing the disease. These include:
- Age: Breast cancer risk increases with age.
- Gender: Breast cancer is much more common in women than in men.
- Family history: If you have a close family member with breast cancer, your risk is higher.
- Genetic mutations: Some women inherit genetic mutations that increase their risk of breast cancer.
- Dense breast tissue: Women with dense breast tissue have a higher risk of breast cancer.
- Lifestyle factors: Certain lifestyle factors, such as obesity, lack of exercise, and alcohol consumption, can also increase your risk of breast cancer.
How is breast cancer diagnosed?
If you have any of the symptoms of breast cancer, it is important to see a doctor right away. Your doctor will perform a physical exam and may order imaging tests, such as a mammogram or ultrasound, to get a better look at the breast tissue. If these tests suggest that you may have breast cancer, your doctor will order a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
How is breast cancer treated?
Treatment for breast cancer will vary depending on the stage and type of cancer, as well as your individual health and preferences. Common treatment options include:
- Surgery: Surgery to remove the tumor and some surrounding tissue is often the first step in treating breast cancer.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body.
- Hormone therapy: Hormone therapy blocks the effects of hormones that can stimulate the growth of cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy drugs work by targeting specific molecules that are involved in the growth and survival of cancer cells.
What is the prognosis for breast cancer?
The prognosis for breast cancer depends on a number of factors, including the stage and type of cancer, as well as your individual health and treatment response. However, early detection and treatment can lead to very good outcomes for most women with breast cancer.
How can I prevent breast cancer?
There is no surefire way to prevent breast cancer, but there are some things you can do to reduce your risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Exercise regularly.
- Eat a healthy diet.
- Limit alcohol consumption.
- Don’t smoke.
- Get regular mammograms and breast exams.
What resources are available for women with breast cancer?
There are a number of resources available to support women with breast cancer and their families. These include:
- Non-profit organizations: There are a number of non-profit organizations that provide information and support to women with breast cancer, such as the American Cancer Society and Susan G. Komen for the Cure.
- Cancer centers: Many cancer centers offer support groups and other resources for women with breast cancer and their families.
- Online communities: There are a number of online communities where women with breast cancer can connect with each other for support and advice.
If you have been diagnosed with breast cancer, it is important to remember that you are not alone. There are many people who care about you and want to help you through this journey.

