What is ADHD?
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects how people perceive and respond to information. It is one of the most common mental disorders in children, affecting about 1 in 10 children worldwide. ADHD can also persist into adulthood, affecting about 2.5% of adults.
While ADHD is a global problem, it is often underdiagnosed and undertreated in Africa. This is due to a number of factors, including lack of awareness of ADHD, stigma associated with mental illness, and limited access to healthcare services.
Prevalence of ADHD in Africa
The prevalence of ADHD in Africa is estimated to be around 7.5%. This is similar to the prevalence of ADHD in other parts of the world, but it is important to note that there is limited research on ADHD in Africa, so the true prevalence of the disorder may be higher.
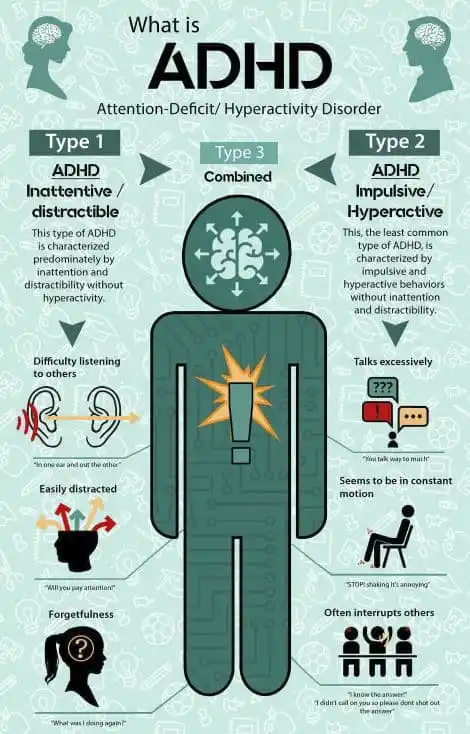
There are three main types of ADHD:
- Predominantly inattentive type: People with this type of ADHD have difficulty paying attention, focusing on tasks, and following through on instructions.
- Predominantly hyperactive-impulsive type: People with this type of ADHD have difficulty sitting still, fidgeting a lot, and acting without thinking.
- Combined type: People with this type of ADHD have symptoms of both inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity.
Causes of ADHD
The exact cause of ADHD is unknown, but it is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some studies have shown that ADHD can be passed down through families, suggesting that there is a genetic component to the disorder. Other studies have shown that exposure to certain environmental factors, such as lead poisoning or prenatal tobacco exposure, can increase the risk of developing ADHD.
Symptoms of ADHD
The symptoms of ADHD can vary depending on the type of ADHD and the severity of the disorder. However, some common symptoms of ADHD include:
- Inattention: Difficulty paying attention, forgetting things easily, and being easily distracted.
- Hyperactivity: Fidgeting a lot, being unable to sit still, and running or climbing excessively.
- Impulsivity: Acting without thinking, having difficulty waiting for turns, and interrupting others.
Diagnosis of ADHD
ADHD is typically diagnosed by a mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist. The diagnosis is based on a comprehensive assessment of the person’s symptoms, medical history, and developmental history. The mental health professional may also use standardized tests to assess the person’s attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity.
Challenges of diagnosing and treating ADHD in Africa
There are a number of challenges associated with diagnosing and treating ADHD in Africa. One challenge is the lack of awareness of ADHD among healthcare providers and the general public. Many people in Africa are not familiar with the symptoms of ADHD, and they may mistake them for signs of laziness, disobedience, or bad behaviour.
Another challenge is stigma associated with mental illness in many African cultures. Mental illness is often seen as a sign of weakness or spiritual weakness, and people with mental disorders may be shunned or discriminated against. This can make it difficult for people with ADHD to seek help for their condition.
Finally, access to healthcare services is limited in many parts of Africa. This can make it difficult for people with ADHD to get the diagnosis and treatment they need.
Treatment of ADHD
There is no one-size-fits-all treatment for ADHD. The best treatment approach for a particular person will depend on the severity of their symptoms, the type of ADHD they have, and their individual needs.
Common treatments for ADHD include:
- Medication: Stimulant medications, such as Ritalin and Adderall, are the most common type of medication used to treat ADHD. These medications can help to improve attention, focus, and impulse control.
- Therapy: Behavioural therapy can help people with ADHD to learn coping skills and strategies for managing their symptoms. Therapy can also help people with ADHD to develop social skills and to improve their academic performance.
- Education: Educating people with ADHD about their disorder and available treatments can help them to manage their symptoms and to live more fulfilling lives.
Impact of ADHD in Africa
ADHD can have a significant impact on a person’s life. Children with ADHD may have difficulty in school, and they may be more likely to engage in risky behaviours. Adults with ADHD may have difficulty keeping a job, maintaining relationships, and managing their finances.
ADHD can also have a negative impact on society as a whole. Children with ADHD are more likely to drop out of school, and they are more likely to commit crimes. Adults with ADHD are more likely to be unemployed and to live in poverty.
Living with ADHD
ADHD can be a challenging disorder to live with, but there are many things that people with ADHD can do to manage their symptoms and to live successful lives. Here are a few tips:
- Find a treatment plan that works for you: Work with your doctor or mental health professional to develop a treatment plan that is right for you. This plan may include medication, therapy, or a combination of both.
- Educate yourself about ADHD: The more you know about ADHD, the better equipped you will be to manage your symptoms and live a successful life.
- Develop coping skills: There are many coping skills that can help people with ADHD to manage their symptoms. These skills can include things like time management, organization, and stress management.
- Build a support system: Having a strong support system can be very helpful for people with ADHD. This support system may include family members, friends, teachers, or therapists.
What can be done to address ADHD in Africa
There are a number of things that can be done to address ADHD in Africa. One important step is to increase awareness of ADHD among healthcare providers and the general public. This can be done through educational campaigns and public service announcements.
Another important step is to reduce the stigma associated with mental illness. This can be done by educating people about the causes and symptoms of mental disorders, and by promoting the idea that mental illness is a treatable medical condition.
Finally, it is important to improve access to healthcare services for people with ADHD. This can be done by increasing the number of mental health professionals in Africa, and by making healthcare more affordable and accessible.
Conclusion
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects how people perceive and respond to information. It is a common disorder that affects both children and adults. The symptoms of ADHD can vary depending on the type of ADHD and the severity of the disorder. There is no one-size-fits-all treatment for ADHD, but common treatments include medication, therapy, and education. People with ADHD can manage their symptoms and live successful lives with the right treatment plan and support system.
You can read more on ADHD here.